Cdif
cdif - context diff command
This project is maintained by kaz-utashiro
CDIF
is word context visualizer of DIFF output
for ANSI color terminal
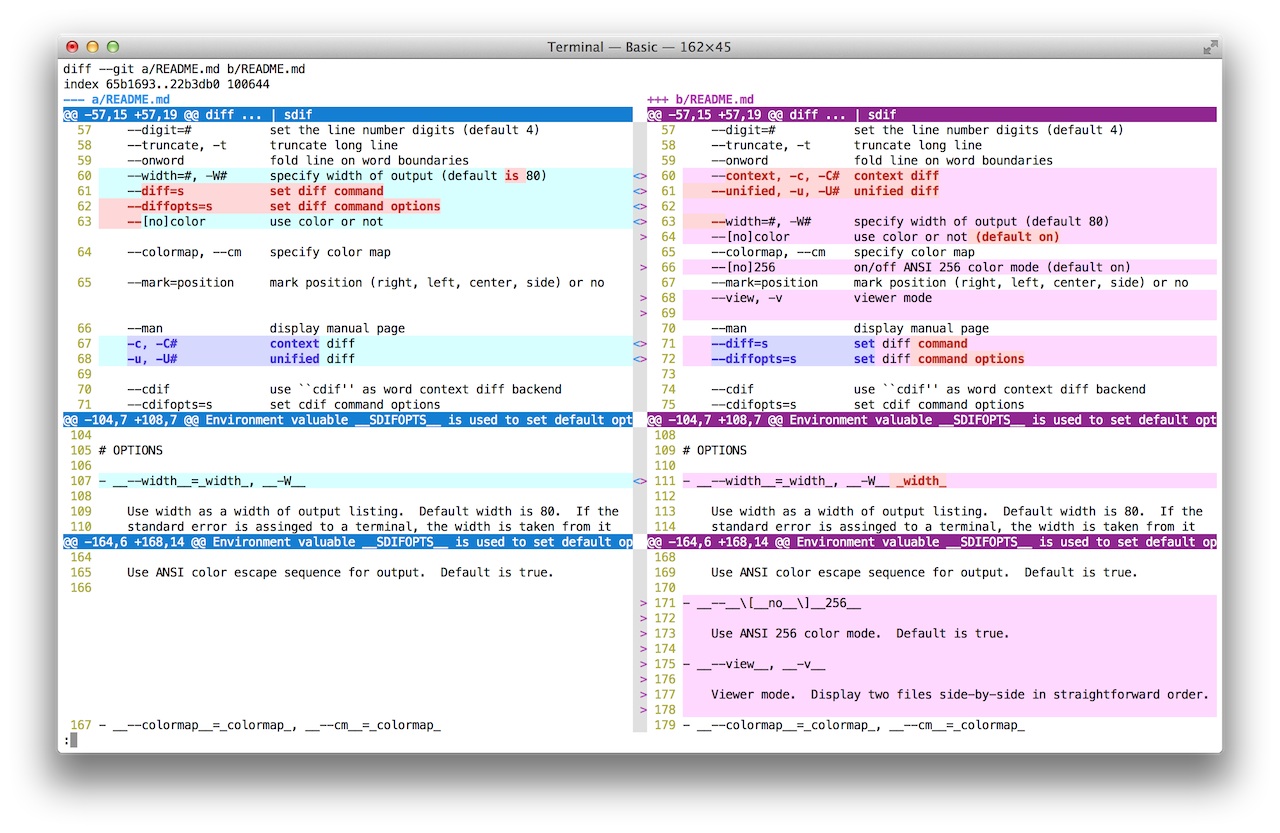
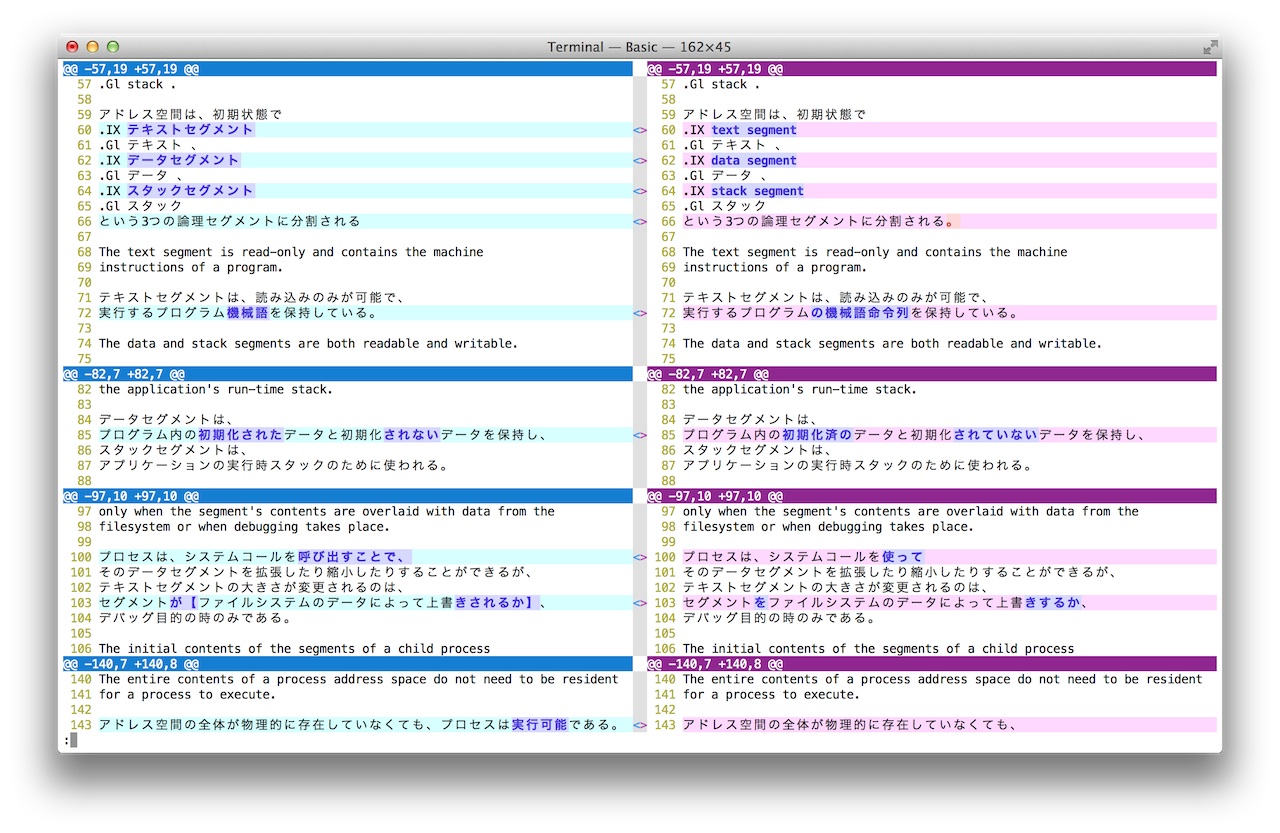
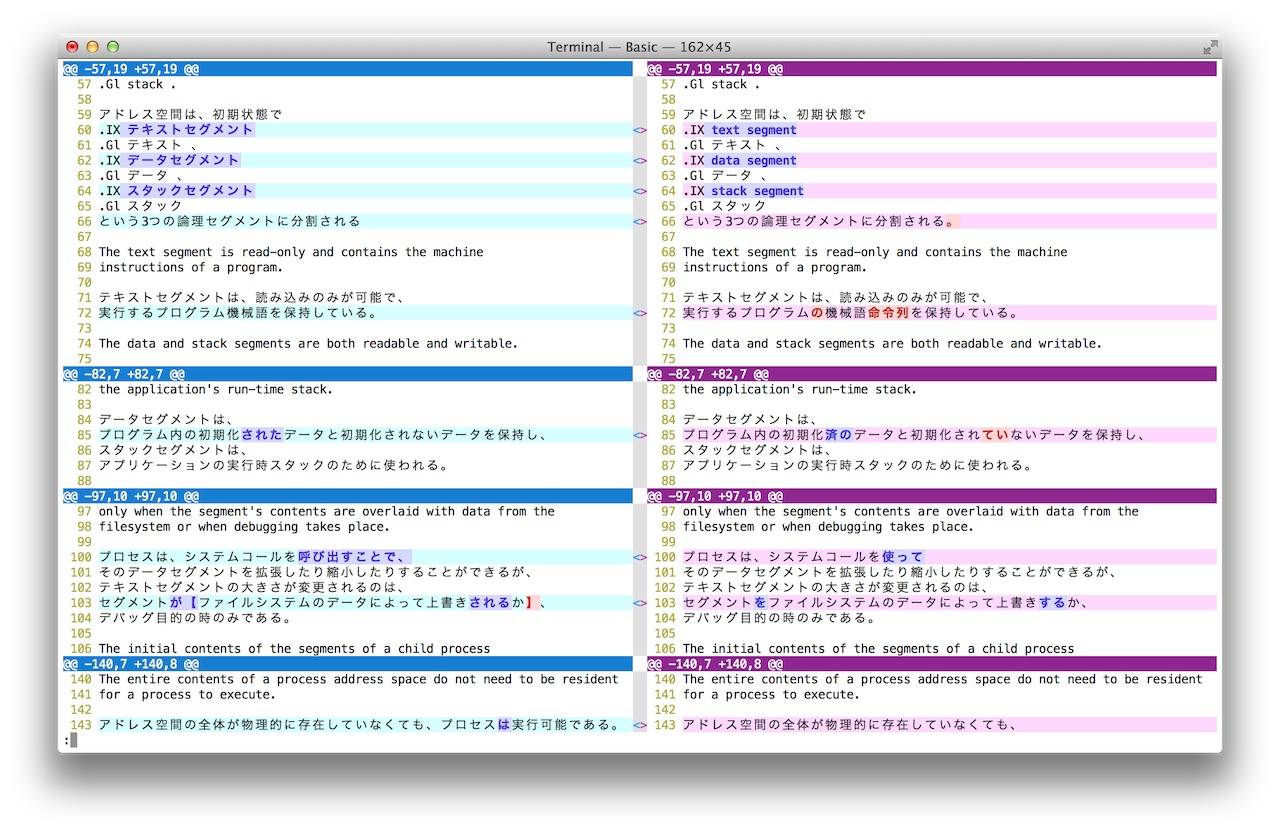
Side-by-side view
power by SDIF command
International
Unicode
East Asian wide width character
Japanese Kanji/Hiragana/Katakana separation
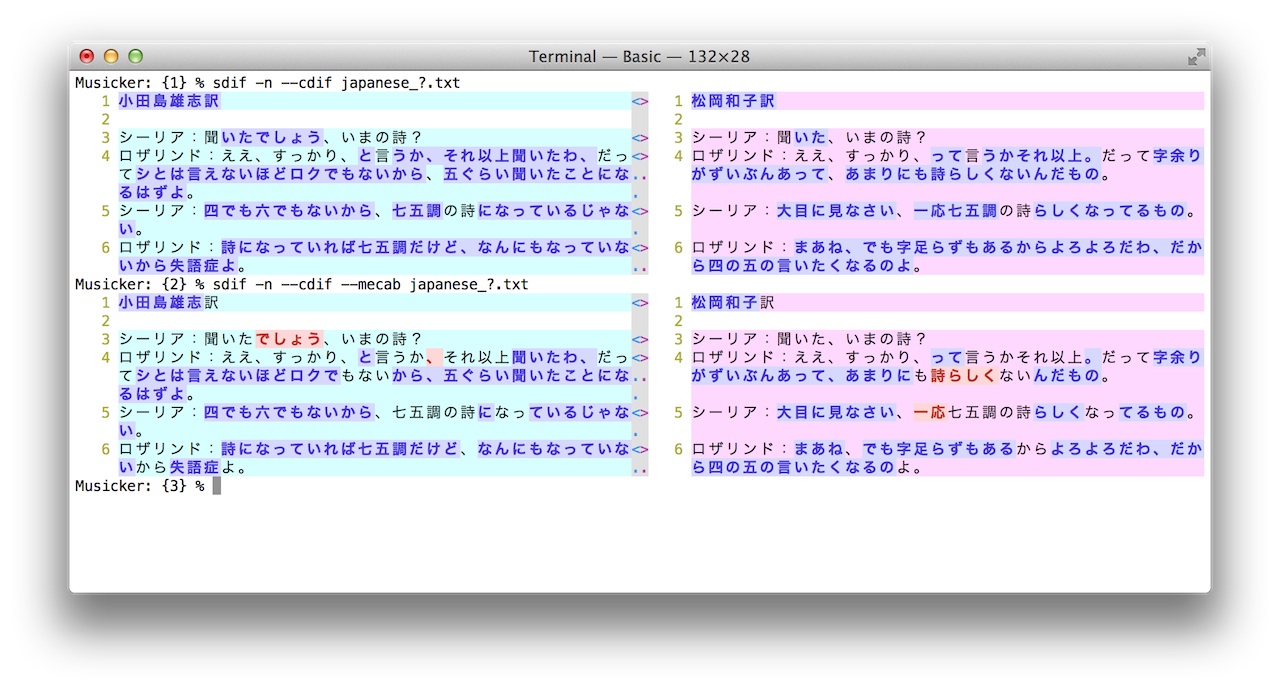
Japanese syllable tokenizer
–mecab morphology
Using inside Emacs
NAME
cdif - word context diff
SYNOPSIS
cdif [cdif option] file1 file2
cdif [rcs options] [cdif options] file
cdif [cdif options] [diff-data]
Options:
-c, -Cn context diff
-u, -Un unified diff
-i ignore case
-b ignore trailing blank
-w ignore whitespace
-t expand tabs
-T initial tabs
--rcs use rcsdiff
-r<rev>, -q rcs options
-B char-by-char comparison
-W specify terminal width
--diff=command specify diff command
--stat show statistical information
--colormap=s specify color map
--[no]color color or not (default true)
--[no]256 ANSI 256 color mode (default true)
--[no]commandcolor color for command line (default true)
--[no]markcolor color for diff mark (default true)
--[no]textcolor color for normal text (default true)
--[no]old print old text (default true)
--[no]new print new text (default true)
--[no]command print diff command line (default true)
--[no]unknown print unknown line (default true)
DESCRIPTION
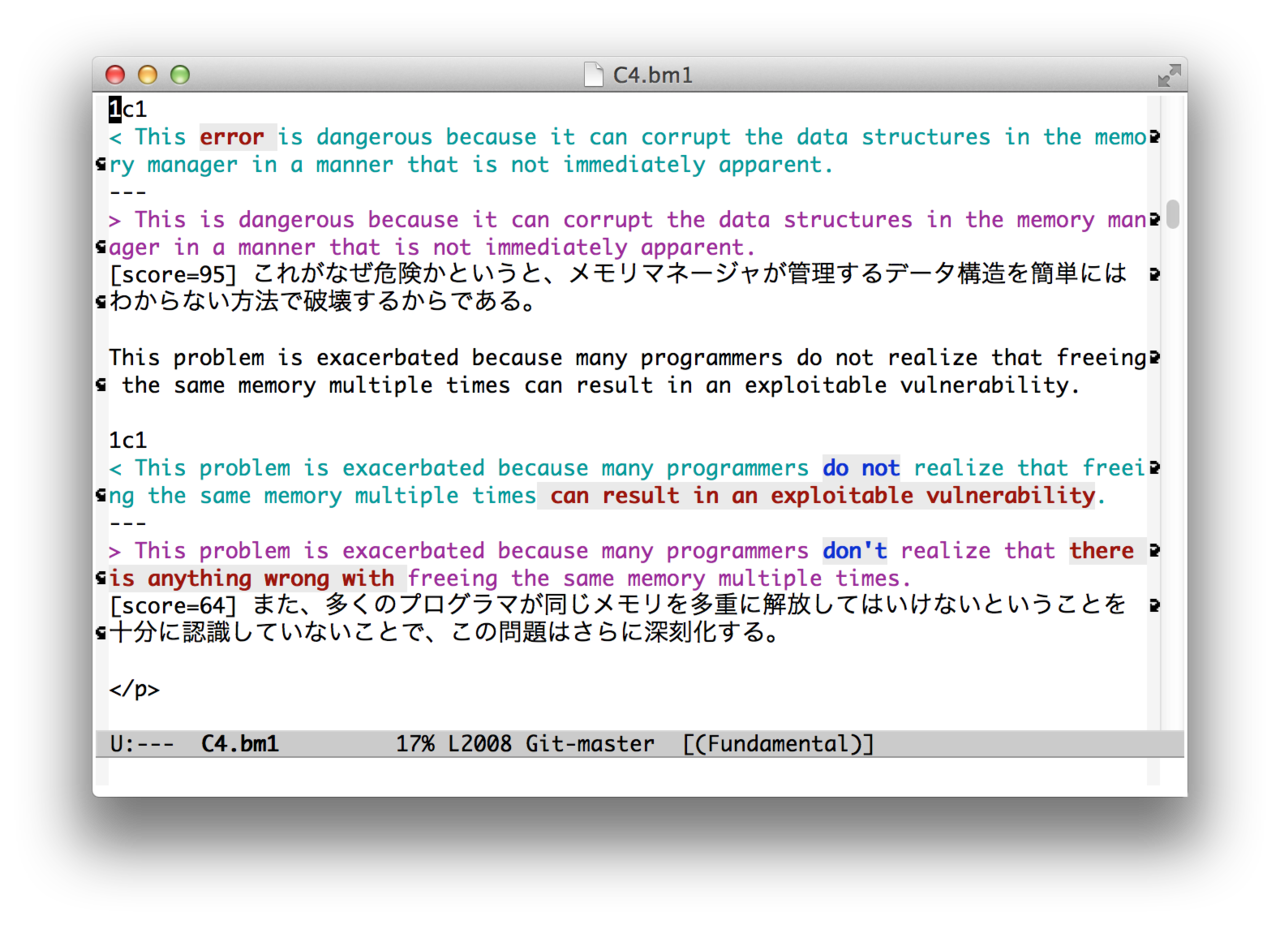
cdif is a post-processor of the Unix diff command. It highlights deleted, changed and added words based on word context.
You may want to compare character-by-character rather than word-by-word. Option -B option can be used for that purpose.
If only one file is specified, cdif reads that file (stdin if no file) as a output from diff command.
Lines those don’t look like diff output are simply ignored and printed.
OPTIONS
-
-[cCuUibwtT]
Almost same as diff command.
-
–rcs, -rrev, -q
Use rcsdiff instead of normal diff. Option –rcs is not required when -rrev is supplied.
-
-B, –char
Compare the data character-by-character context.
-
-W width, –width=width
Explicitly specify terminal width.
-
–diff=command
Specify the diff command to use.
-
–[no]color
Use ANSI color escape sequence for output.
-
–colormap=colormap, –cm=colormap
Basic colormap format is :
FIELD=COLORwhere the FIELD is one from these :
COMMAND Command line OMARK Old mark NMARK New mark OTEXT Old text NTEXT New text OCHANGE Old change part NCHANGE New change part APPEND Appended part DELETE Deleted partand additional Common and Merged FIELDs for git-diff combined format.
CMARK Common mark CTEXT Common text MMARK Merged mark MTEXT Merged textYou can make multiple fields same color joining them by = :
FIELD1=FIELD2=...=COLORAlso wildcard can be used for field name :
*CHANGE=BDwMultiple fields can be specified by repeating options
--cm FILED1=COLOR1 --cm FIELD2=COLOR2 ...or combined with comma (,) :
--cm FILED1=COLOR1,FIELD2=COLOR2, ...COLOR is combination of single character representing uppercase foreground color :
R Red G Green B Blue C Cyan M Magenta Y Yellow K Black W Whiteand alternative (usually brighter) colors in lowercase :
r, g, b, c, m, y, k, wor RGB values and 24 grey levels if using ANSI 256 or full color terminal :
FORMAT: foreground[/background] COLOR: 000 .. 555 : 6 x 6 x 6 216 colors 000000 .. FFFFFF : 24bit RGB mapped to 216 colors L00 .. L23 : 24 grey levels Sample: 005 0000FF : blue foreground /505 /FF00FF : magenta background 000/555 000000/FFFFFF : black on white 500/050 FF0000/00FF00 : red on greenand other effects :
S Stand-out (reverse video) U Underline D Double-struck (boldface) F Flash (blink) E Expand (only for command line)When E is specified for command line, the line is expanded to window width filling up by space characters.
Defaults are :
COMMAND => "SE" OMARK => "CS" NMARK => "MS" OTEXT => "C" NTEXT => "M" OCHANGE => "BD/445" NCHANGE => "BD/445" DELETE => "RD/544" APPEND => "RD/544" CMARK => "GS" MMARK => "YS" CTEXT => "G" MTEXT => "Y"This is equivalent to :
cdif --cm 'COMMAND=SE,OMARK=CS,NMARK=MS' \ --cm 'OTEXT=C,NTEXT=M,*CHANGE=BD/445,DELETE=APPEND=RD/544' \ --cm 'CMARK=GS,MMARK=YS,CTEXT=G,MTEXT=Y' - –[no]commandcolor, –cc
- –[no]markcolor, –mc
-
–[no]textcolor, –tc
Enable/Disable using color for the corresponding field.
-
–[no]old, –[no]new
Print or not old/new text in diff output.
-
–[no]command
Print or not command lines preceding diff output.
-
–[no]unknown
Print or not lines not look like diff output.
-
–[no]mark
Print or not marks at the top of diff output lines. At this point, this option is effective only for unified diff.
Next example produces the output exactly same as new except visual effects.
cdif -U100 --nomark --noold --nocommand --nounknown old newThese options are prepared for watchdiff(1) command.
-
–stat
Print statistical information at the end of output. It shows number of total appended/deleted/changed words in the context of cdif. It’s common to have many insertions and deletions of newlines because of text filling process. So normal information is followed by modified number which ignores insert/delete newlines.
-
–mecab
Experimental option for using mecab as a tokenizer. To use this option, external command mecab has to be installed.
AUTHOR
Kazumasa Utashiro
https://github.com/kaz-utashiro/cdif
SEE ALSO
perl(1), diff(1), sdif(1), watchdiff(1)
BUGS
cdif is naturally not very fast because it uses normal diff command as a back-end processor to compare words.
COPYRIGHT
Use and redistribution for ANY PURPOSE are granted as long as all copyright notices are retained. Redistribution with modification is allowed provided that you make your modified version obviously distinguishable from the original one. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS’’ AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES ARE DISCLAIMED.